Aluminum is one of the most versatile materials in modern industry, valued for its combination of light weight, corrosion resistance, and excellent workability. From aerospace components to consumer electronics and architectural designs, its adaptability comes from a diverse range of alloys and processing methods. Choosing the right aluminum alloy is not just a matter of knowing aluminum properties—it requires a clear understanding of industry-specific performance needs and the production capabilities of your aluminum manufacturer or aluminum supplier.
The useful properties of aluminum—including its high strength-to-weight ratio, electrical and thermal conductivity, and recyclability—make it a preferred choice across multiple fields. However, different industries require different balances of these traits, and in many cases, the decision involves trade-offs between cost, machinability, and performance.
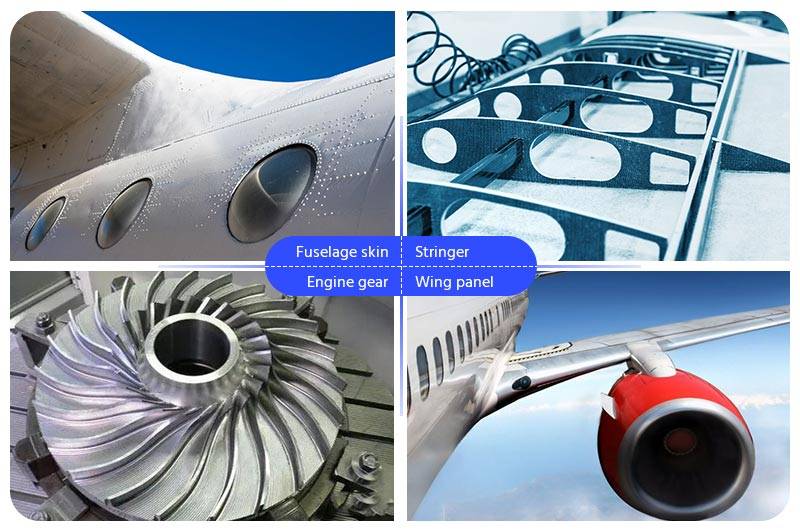
Aerospace: Extreme Light Weight and High Strength
In aerospace engineering, reducing structural weight without compromising strength is critical. A 1% reduction in aircraft weight can lead to fuel savings of around 0.75%, which significantly impacts operating costs over an aircraft’s service life. This makes high-strength aluminum alloys indispensable.
Key alloys for aerospace use include 2024 and 7075, known for their excellent strength and fatigue resistance. These alloys are often used in wing structures, fuselage frames, and landing gear components. Heat treatment enhances their performance, but engineers must also consider susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking, especially in marine-flight environments.
| Alloy | Strength (MPa) | Corrosion Resistance | Common Uses |
| 2024 | 470–480 | Moderate | Fuselage skins, wing structures |
| 7075 | 540–570 | Low to Moderate | Landing gear, structural fittings |
When sourcing from an aluminum manufacturer, aerospace companies require strict quality certifications such as AS9100 and full traceability. The decision-making process should also account for aluminium characteristics and properties like fatigue resistance under cyclic loads.
Automotive: Lightweight, Formability, and Cost Efficiency
The automotive industry uses aluminum to reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency, and meet stricter emissions targets. A 10% weight reduction can improve fuel economy by 6–8%. Here, die cast aluminum material properties are especially important for engine blocks, transmission housings, and structural parts, thanks to their ability to create complex shapes at high production volumes.
Common automotive alloys include ADC12 (for die casting), 6061, and 6082 (for structural parts). While 6061 offers good corrosion resistance and weldability, ADC12 excels in casting precision and dimensional stability.
| Alloy | Process | Key Benefit | Typical Component |
| ADC12 | Die Casting | High dimensional accuracy | Engine blocks |
| 6061 | Extrusion/Welding | Corrosion resistance | Body panels |
| 6082 | Extrusion | High strength | Chassis components |
Automakers working with an aluminum supplier must balance cost and performance, often opting for aluminum wholesale purchases to reduce material costs for high-volume production runs.

Electronics & Heat Dissipation: High Thermal Conductivity and Machinability
Electronics and heat management systems benefit from aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, which ranges from 200–235 W/m·K depending on the alloy. Pure aluminum grades such as 1050 and 1350 are common for heat sinks, electrical bus bars, and LED housings. These alloys are easy to machine, ensuring design flexibility for compact, high-density components.
Case Example: A laptop manufacturer switched from copper to aluminum heat sinks, reducing device weight by 35% while maintaining cooling efficiency, leading to lower shipping costs and improved user comfort.
However, pure aluminum is mechanically weaker than alloyed grades, so designs must consider structural support when needed. For more demanding structural-electronic applications, 6063 offers a balance between conductivity and strength.

Food & Beverage Packaging: Hygiene, Non-Toxicity, and Barrier Properties
In the food and beverage sector, aluminum is valued for its non-toxic, corrosion-resistant, and hygienic qualities. It forms a natural oxide layer that prevents chemical reactions with most food products, ensuring taste preservation and safety. The useful properties of aluminum in this field include light weight for reduced transportation costs, complete recyclability, and excellent barrier protection against light, oxygen, and moisture.
Common alloys such as 3003 and 8011 are used in beverage cans, food trays, and foil packaging. For example, 8011 aluminum foil is widely used for yogurt lids and pharmaceutical blister packs because of its sealing ability and formability.
| Alloy | Key Feature | Typical Application |
| 3003 | Corrosion resistance, formability | Food containers, cooking utensils |
| 8011 | Excellent barrier properties, sealing | Foil wraps, beverage seals |
When working with an aluminum manufacturer or aluminum supplier for food applications, compliance with standards such as FDA (USA) or EU food contact regulations is critical. Processing lines must avoid contamination to maintain hygienic integrity. Aluminum wholesale procurement can help large-scale food producers reduce packaging costs while ensuring material traceability.

Architecture & Structural Use: Aesthetics, Weather Resistance, and Low Maintenance
In architectural and structural applications, corrosion resistance, surface appearance, and long service life are top priorities. Alloys such as 6063 and 5052 are commonly used in window frames, curtain walls, and decorative facades due to their excellent anodizing response and durability in outdoor environments.
Architects often work closely with aluminum manufacturers to specify finishes—powder coating, anodizing, or PVDF coatings—to enhance aesthetics while reducing maintenance costs. For example, anodized aluminum curtain walls can maintain appearance for over 20 years with minimal upkeep, even in harsh urban climates.

Marine & Offshore: Salt Spray Resistance and Weldability
Marine environments present one of the most aggressive corrosion challenges for metals due to constant salt exposure. 5083 and 5754 alloys are widely used for boat hulls, offshore platforms, and deck structures thanks to their high magnesium content, which provides excellent resistance to seawater corrosion.
| Alloy | Key Advantage | Common Application |
| 5083 | Exceptional seawater resistance | Boat hulls, ship superstructures |
| 5754 | Good corrosion resistance & formability | Offshore platforms, tankers |
These alloys are also weldable, allowing for large structural assemblies without compromising corrosion performance. Working with an experienced aluminum supplier is essential to ensure proper material storage and handling, as contamination before welding can cause localized corrosion failures.
Final Advices
Selecting the right aluminum alloy for your industry requires more than knowing the useful properties of aluminum—it involves matching specific aluminium characteristics and properties to the functional, environmental, and economic demands of your application. Whether sourcing high-strength aerospace alloys, precision die cast aluminum material properties for automotive components, or corrosion-resistant grades for marine use, partnering with a reliable aluminum manufacturer or aluminum wholesale supplier ensures consistent quality and long-term performance. If you have no ideas, please consider CHAL.
By aligning your material choice with proven industry data, production methods, and supplier expertise, you can achieve both performance goals and cost efficiency in any field.