Aluminum alloys are ubiquitous in various industries due to their remarkable properties such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio. Among these alloys, the 70 series stands out for its exceptional performance in demanding applications. In this article, we delve into a comparative analysis between two prominent members of the 70 series: Aluminum 7050 and Aluminum 7075.

What is 70 Series Aluminum?
The term “70 series aluminum” typically refers to aluminum alloys that belong to the 7000 series, which are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio. These alloys are often used in applications where strength, hardness, and toughness are crucial, such as in aerospace, automotive, and structural engineering.
Some common alloys within the 7000 series include:
- 7075: 7075 aluminum alloy is one of the most well-known alloys in the 7000 series. It offers excellent strength comparable to many steels while maintaining relatively good corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in aircraft structures, where strength and low weight are critical.
- 7050: Similar to 7075, 7050 aluminum alloy offers high strength, good corrosion resistance, and good machinability. It is often used in aerospace applications and structural components.
- 7049: This alloy offers high strength and good corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in aerospace applications, particularly in aircraft wing and fuselage structures.
These alloys typically undergo various heat treatments to achieve the desired combination of properties, such as strength, hardness, and toughness. However, while they offer excellent mechanical properties, they may not be as easily formable or weldable as some other aluminum alloys.
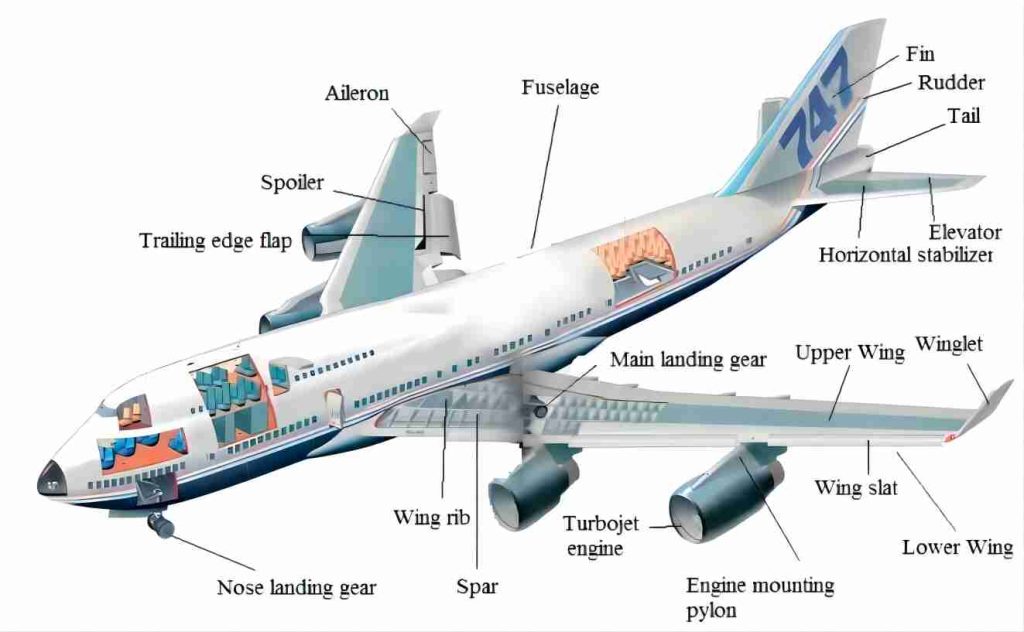
Why Choosing 70 Series Aluminum?
Choosing 70 series aluminum, particularly alloys like 7075 or 7050, offers several advantages for various applications:
- High Strength: 70 series aluminum alloys are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. They provide high tensile strength, making them suitable for applications where structural integrity and load-bearing capacity are crucial.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is inherently lightweight, and alloys within the 70 series maintain this characteristic while offering superior strength. This makes them ideal for applications where reducing weight without compromising performance is essential, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: While not as corrosion-resistant as some other aluminum alloys like the 6000 series, 70 series aluminum still offers good resistance to corrosion. This property ensures durability and longevity, particularly in outdoor or harsh environments.
- Machinability: Certain 70 series alloys, like 7050, exhibit good machinability characteristics. This makes them easier to work with during manufacturing processes such as milling, drilling, and turning, allowing for precise component fabrication.
- High Stress Applications: Due to their high strength and toughness, 70 series aluminum alloys are suitable for use in high-stress applications, including aerospace structures, automotive components, bicycle frames, and high-performance sporting goods.
- Heat Treatability: Alloys within the 70 series can be subjected to various heat treatments to further enhance their mechanical properties. Heat treatments such as solution heat treatment, quenching, and aging can be employed to achieve specific strength levels and desired performance characteristics.
- Resilience: These alloys often exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, which is crucial in applications subject to cyclic loading or repeated stress, such as aircraft structures and automotive suspension components.
Overall, the choice of 70 series aluminum is dictated by the specific requirements of the application, where the combination of strength, lightweight, corrosion resistance, and machinability make it an attractive option for many industries.

Differences between Aluminum 7050 vs 7075
Aluminum alloys 7050 and 7075 are both high-strength materials commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and structural applications. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in terms of composition, properties, and applications. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Composition:
- 7050 Aluminum Alloy: The main alloying elements in 7050 aluminum are zinc and magnesium, with small additions of copper and chromium. This composition provides excellent strength and stress corrosion cracking resistance.
- 7075 Aluminum Alloy: 7075 aluminum contains zinc as the primary alloying element, with smaller amounts of magnesium and copper. It also has trace amounts of other elements such as chromium and manganese. This alloy composition results in high strength and good machinability.
2. Strength:
- 7050 Aluminum: 7050 aluminum offers slightly lower strength compared to 7075, but it still provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It has a typical ultimate tensile strength of around 510 MPa (74,000 psi) and a yield strength of about 455 MPa (66,000 psi).
- 7075 Aluminum: 7075 aluminum is one of the highest strength aluminum alloys available commercially. It has an ultimate tensile strength ranging from 570 to 700 MPa (83,000 to 102,000 psi) and a yield strength of around 500 MPa (73,000 psi).
3. Corrosion Resistance:
Both alloys offer good corrosion resistance, but 7050 may have slightly better resistance to stress corrosion cracking due to its magnesium content. However, both alloys may require protective coatings or surface treatments for prolonged exposure to corrosive environments.
4. Machinability:
- 7050 Aluminum: While 7050 aluminum is generally more difficult to machine compared to some other aluminum alloys, it can still be machined effectively with the appropriate tools and techniques.
- 7075 Aluminum: 7075 aluminum has better machinability compared to 7050, making it more suitable for applications requiring intricate machining operations. However, it may still pose challenges compared to lower-strength aluminum alloys.
5. Applications:
- 7050 Aluminum: Common applications for 7050 aluminum include aircraft structural components, such as wing spars and fuselage frames, as well as high-performance bicycle frames, and high-strength structural parts in the automotive industry.
- 7075 Aluminum: 7075 aluminum is widely used in aerospace applications, including aircraft fuselage frames, wing structures, and helicopter rotor components. It is also used in high-performance bicycle frames, automotive parts, and in high-stress structural applications where strength and toughness are critical.
In summary, while both 7050 and 7075 aluminum alloys offer high strength and good corrosion resistance, the choice between them depends on specific application requirements such as strength levels, machinability, and environmental conditions.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between Aluminum 7050 and Aluminum 7075 ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application. While Aluminum 7075 offers superior strength properties, Aluminum 7050 excels in toughness and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Engineers and manufacturers must carefully assess the performance characteristics and environmental factors to select the most suitable alloy for their intended use. Nonetheless, both Aluminum 7050 and Aluminum 7075 exemplify the remarkable capabilities of the 70 series aluminum alloys in meeting the demanding needs of modern industries. If you are looking for a 7050 and 7075 aluminum supplier, please feel free to contact CHAL, believe they will not let you down.