Aluminum sheet metal is a versatile material used in a wide range of applications, from construction and automotive to aerospace and DIY projects. Cutting aluminum sheet metal may seem like a daunting task, but with the right methods and techniques, it can be a straightforward and efficient process. In this article, we will explore various methods for cutting aluminum sheet metal and provide tips for achieving precise and clean cuts.

Tools for Cutting Aluminum Sheet Metal
Hand Tools for Cutting Aluminum Sheet Metal
- Snips:
Hand snips, also known as aviation snips, are an excellent choice for cutting aluminum sheet metal with precision. These come in three types: straight-cut, left-cut, and right-cut. Choose the appropriate type based on the direction of the cut you need. Make sure to wear safety gloves, and follow the natural curve of the snips for smoother cuts.

- Hacksaw:
A hacksaw with a fine-toothed blade can be used to cut aluminum sheet metal. Secure the sheet in a stable position and use long, steady strokes. Apply a cutting lubricant to reduce friction and prevent the blade from overheating. This method is suitable for thinner aluminum sheets.
Power Tools for Cutting Aluminum Sheet Metal
- Circular Saw:
A circular saw equipped with a carbide-tipped blade designed for non-ferrous metals is a fast and efficient way to cut aluminum sheet metal. Set the blade depth to just below the thickness of the sheet and use a straight edge as a guide for straight cuts.

- Jigsaw:
A jigsaw with a metal-cutting blade can be used for curved or irregular cuts in aluminum sheet metal. Secure the sheet and start cutting with a slow and steady motion. This method is ideal for intricate designs.
- Band Saw:
A band saw with a fine-toothed blade is suitable for straight and curved cuts in aluminum sheet metal. Ensure that the blade is designed for non-ferrous metals, and adjust the speed to prevent overheating.
Specialized Techniques for Cutting Aluminum Sheet Metal
- Plasma Cutting:
For industrial applications and thicker aluminum sheets, plasma cutting offers a precise and efficient solution. Plasma cutters use a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and cut through the metal. This method is suitable for complex shapes and thick aluminum sheets.
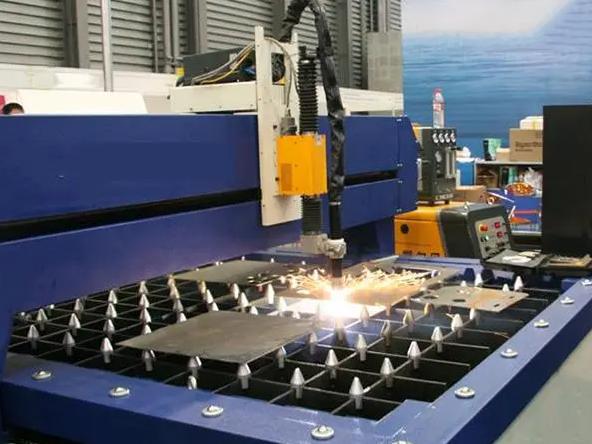

- Waterjet Cutting:
Waterjet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through aluminum sheet metal. This method produces clean and precise cuts without generating heat, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.

5 Tips for Efficient Cutting:
- Safety First: Always wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and eye protection, to prevent injuries.
- Secure the Sheet: Ensure that the aluminum sheet is securely clamped or anchored to prevent movement during cutting.
- Cutting Lubricant: Use a cutting lubricant or coolant to reduce friction and heat during the cutting process, resulting in cleaner cuts and prolonging tool life.
- Choose the Right Blade: Select the appropriate blade or cutting tool for the thickness and type of aluminum sheet metal you are working with.
- Practice on Scrap: If you’re new to cutting aluminum, practice on scrap pieces to familiarize yourself with the chosen method and achieve the desired precision.
How to Choose the Proper Cutting Technology? Thickness is a Main Factor
Aluminum sheet metal thickness plays a significant role in determining the most suitable cutting technology. Here’s how it impacts the selection:
For Cutting Speed and Efficiency:
- Thinner sheets (up to 3mm): Can be cut with high speed and efficiency using technologies like laser cutting, which excels in this range. Plasma and water jet cutting are also options, but laser tends to be faster and cleaner.
- Medium thickness sheets (3-6mm): Require slower cutting speeds compared to thinner sheets. Laser remains a good option, but speed adjustments and potentially higher power may be needed. Plasma and water jet cutting become more competitive in this range due to their ability to handle thicker materials.
- Thicker sheets (6mm+): Often favor technologies like plasma and water jet cutting. Plasma can handle thicker sheets (up to 50mm), while water jet offers precision and minimal heat-affected zone for even the thickest sheets. Laser cutting becomes less efficient for very thick materials.
For Cut Quality and Edge Finish:
- Thinner sheets: Laser cutting generally provides the best edge finish with minimal heat distortion and narrow kerfs (cut width). Plasma and water jets can also produce good quality cuts, but kerfs may be wider, and water jets might require secondary finishing for some applications.
- Medium thickness sheets: Similar to thinner sheets, laser retains its advantage in cut quality, although kerfs and heat-affected zones might increase slightly. Plasma and water jet cutting can still be suitable but with some compromise on edge finish compared to laser.
- Thicker sheets: Plasma cutting may leave rougher edges and wider kerfs compared to thinner sheets. Water jet cutting remains a good option for high-precision cuts with minimal heat impact, even for thick materials.
For Cost and Availability:
- Thinner sheets: Laser cutting tends to be more expensive than plasma or water jet cutting for small quantities. However, its speed and precision can make it more cost-effective for large production runs.
- Medium thickness sheets: Costs become more competitive between different technologies. Laser continues to be viable, but plasma and water jet become attractive due to their lower cost and ability to handle thicker materials.
- Thicker sheets: Plasma cutting is often the most affordable option for thick aluminum sheets. Water jet cutting, while offering superior quality, is generally more expensive due to its higher operating costs.
Conclusion
Cutting aluminum sheet metal can be a straightforward task with the right tools and techniques. Whether you opt for hand tools, power tools, or specialized methods, the best cutting technology for aluminum sheet metal depends on a combination of factors: thickness, desired cut quality, speed and efficiency, cost, and complexity of the cuts, etc. Consulting with an aluminum sheet metal fabrication expert can help ensure the right choice for your specific material and application. Following safety guidelines and taking your time will ensure that you achieve accurate and clean cuts for your projects.