Aluminum paste is a versatile industrial material used in various applications. It imparts a metallic look and enhances functionalities in products ranging from paints to explosives. Let’s delve deeper into the world of aluminum paste, exploring its composition, different types, manufacturing process, and safety considerations for handling it.
What is Aluminum Paste?
Aluminum paste is a composite material consisting of microscopic aluminum flakes suspended within a carrier medium. These flakes, typically manufactured from aluminum powder, are incredibly thin and flat, creating a large surface area compared to their mass. The carrier medium can be either organic solvent-based or water-based, depending on the intended application. The specific properties of the aluminum paste, such as reflectivity and opacity, are influenced by the size, shape, and orientation of the aluminum flakes within the carrier.

What are the Key Properties of Aluminum Paste?
Aluminum paste, a versatile and widely used material, possesses several key properties that make it suitable for a broad range of applications. Let’s delve into a detailed exploration of these properties:
- Reflective Property: One of the most notable properties of aluminum paste is its ability to reflect light and heat. The microscopic flakes in the paste act as miniature mirrors, reflecting radiation away from the surface. This property is particularly beneficial in applications that require a captivating metallic finish, such as automotive paints, signage, and displays. The reflective property of aluminum paste not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of these products but also contributes to their functionality by providing a protective layer that deflects harmful radiation.
- Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum paste exhibits good electrical conductivity, a property that finds utility in a variety of applications. In the field of electronics, for instance, aluminum paste is used in the manufacture of conductive adhesives, pastes, and inks. These products are used in a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to solar panels and LED lights.
- Lightweight Nature: Aluminum paste is light, which makes it an ideal material for applications where weight is a concern. This property is particularly beneficial in the automotive and aerospace industries, where reducing the weight of vehicles and aircraft can lead to significant fuel savings.
- Nonmagnetic and Non-sparking Properties: Aluminum paste is nonmagnetic and non-sparking, making it safe for use in environments where sparks could pose a risk, such as in flammable or explosive atmospheres. These properties also make aluminum paste suitable for use in certain medical and scientific applications.
- Malleability and Ductility: Aluminum stands second among metals in the scale of malleability, and sixth in ductility. These properties make aluminum paste easily constructed and shaped, which is beneficial in many industrial applications. For instance, in the packaging industry, aluminum paste is used to create attractive and durable labels and decorations.
- Resistance: Certain types of aluminum paste, such as resin coated aluminum paste, provide heightened resistance to acids, alkalis, weathering, voltage, and other demanding environments. This property makes aluminum paste an ideal material for protective coatings in a variety of industries, from construction and transportation to electronics and energy.
- Adhesive Property: Aluminum paste exhibits excellent adhesion, making it an ideal material for coatings and other applications that require a strong bond. This property is particularly beneficial in the paint industry, where aluminum paste is used to create durable and attractive finishes.
- Design Flexibility: Advanced process technology allows for the creation of aluminum paste with a wide range of silver-metallic colors and design effects. This technology provides closer control and higher uniformity of the microparticle size, together with higher surface smoothness. This property opens up a world of possibilities for designers and manufacturers, enabling them to create products with unique and eye-catching appearances.

What are the Main Types of Aluminum Paste?
Aluminum paste, a versatile material used in a variety of applications, is available in several distinct types, each designed for a specific purpose. Let’s delve into the details of these types:
- Leafing Aluminum Paste: This variant of aluminum paste is characterized by its meticulously aligned aluminum flakes. The unique orientation of these flakes allows them to overlap effectively when applied, thereby maximizing light reflection. The result is a stunning, metallic finish that enhances the aesthetic appeal of a range of products. This type of aluminum paste is commonly used in high-end automotive paints, signage and displays, and foil stamping.
- Non-Leafing Aluminum Paste: Unlike its leafing counterpart, non-leafing aluminum pastes feature flake-shaped microparticles that distribute uniformly into parallel layers throughout the paint or coating layer. This uniform distribution ensures that the color effect of pigments or other coloring materials present in the paint or coating remains fully visible from the outside.
- Design Grade Aluminum Paste: This type of aluminum paste is a product of advanced process technology that enables the creation of previously unattainable levels of surface appearance and visual effects. This technology provides closer control and higher uniformity of the microparticle size, along with higher surface smoothness.
- Resin Coated Aluminum Paste: This variant of aluminum paste offers enhanced resistance to acids, alkalis, weathering, voltage, and other demanding environments, as well as increased bond strength within the paint or coating layer.
It’s important to note that the exact properties and applications of these types of aluminum paste can vary depending on the specific requirements of the end product and the manufacturer’s proprietary methods. Therefore, for the most accurate and detailed information, it’s recommended to consult directly with the manufacturer. This will ensure that you have the most up-to-date and relevant information for your specific needs.

How is Aluminum Paste Manufactured?
Aluminum paste is a material that consists of microscopic flake-shaped aluminum particles finely dispersed in an organic solvent or aqueous-based carrier1. The production process of aluminum paste is meticulous and involves several steps.
- Powder Production: The first step in manufacturing aluminum paste is the production of aluminum powder. This can be achieved through various methods, including atomization, mechanical grinding, or chemical processes. Atomization involves spraying molten aluminum into a chamber where it solidifies into fine droplets, which are then collected and processed into powder form. Mechanical grinding involves crushing aluminum ingots or solid aluminum chunks into smaller particles using crushers and grinders. Chemical processes, such as the reduction of aluminum oxide using a reducing agent like carbon, can also yield aluminum powder.
- Milling: Once the aluminum powder is produced, it undergoes milling to reduce the particle size and achieve the desired fineness. This is typically done using specialized equipment such as ball mills or attritors. In these mills, the aluminum powder is mixed with a solvent and grinding media, such as ceramic or steel balls, which collide with the powder to break down agglomerates and reduce particle size. The milling process may take several hours or even days to achieve the desired particle size distribution.
- Surface Treatment: Surface treatment is a critical step to enhance the reactivity and stability of the aluminum powder. Surface treatments can include the addition of organic or inorganic compounds to the powder surface to modify its properties. Common surface treatments include the application of fatty acids, such as stearic acid, or metal salts, such as aluminum stearate or aluminum oleate. These compounds form a protective layer on the aluminum powder surface, preventing oxidation and improving compatibility with the solvent and other additives used in the paste formulation.
- Dispersion: The milled and surface-treated aluminum powder is then dispersed in a suitable solvent to form a paste. The choice of solvent depends on the intended application of the aluminum paste and factors such as volatility, compatibility with other components, and environmental considerations. Common solvents used for aluminum paste include aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and alcohols. The dispersion process typically involves mixing the aluminum powder with the solvent using high-speed agitation equipment, such as dispersers or homogenizers, to ensure uniform distribution and proper wetting of the powder particles.
- Additives Incorporation: Depending on the desired properties of the final paste, various additives may be incorporated into the formulation. These additives can include rheology modifiers to control viscosity and flow behavior, dispersants to improve particle dispersion and stability, adhesion promoters to enhance adhesion to substrates, and corrosion inhibitors to prevent oxidation of the aluminum particles. The incorporation of additives is typically done during the dispersion stage by mixing them with the solvent and aluminum powder.
- Packaging: Once the aluminum paste is manufactured, it is packaged into suitable containers for storage and transportation. Packaging materials must be compatible with the paste formulation and provide adequate protection against moisture, light, and contamination. Common packaging formats for aluminum paste include metal drums, plastic containers, and flexible pouches. Proper labeling and documentation are also essential to ensure traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
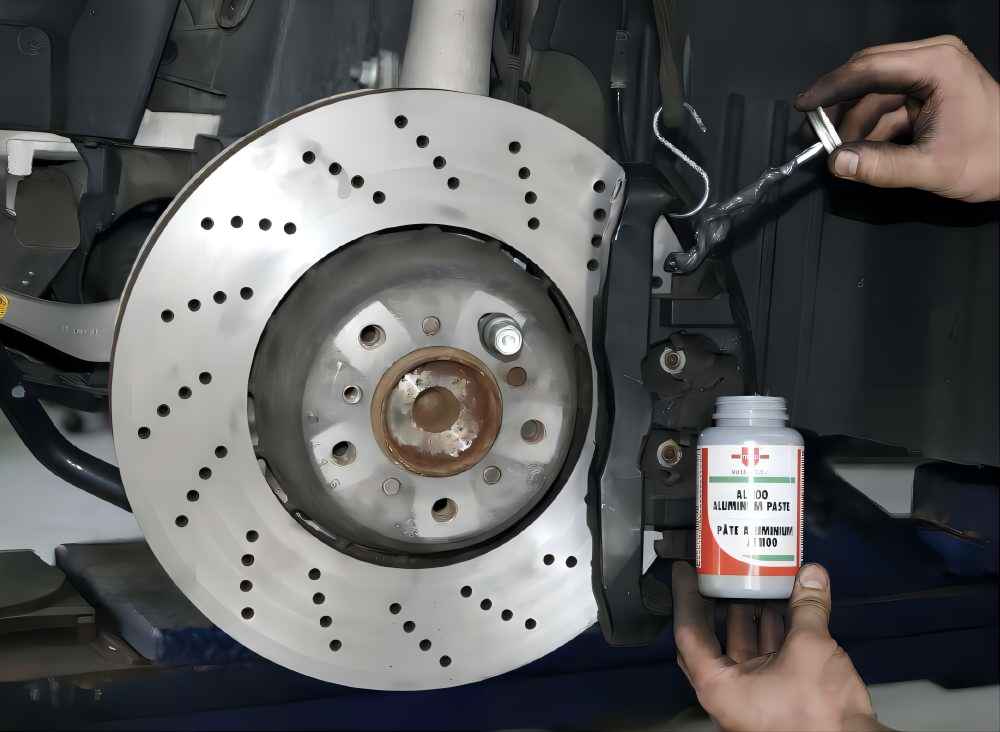

What are the Applications of Aluminum Paste?
Aluminum paste, a material composed of tiny flake-like aluminum particles dispersed in an organic or aqueous carrier, has a wide array of applications across various industries. Here is a detailed exploration of its uses:
- Paints and Coatings: One of the most common uses of aluminum paste is in the paints and coatings industry. The metallic sheen that aluminum paste provides when mixed with paint enhances the aesthetic appeal of the painted surface. This is particularly useful in both industrial and decorative paints. For instance, in the automotive industry, aluminum paste is used in car paints to provide a shiny, metallic finish. It’s also used in protective coatings to prevent corrosion, thereby extending the lifespan of the vehicle.
- Solar Cells: In the renewable energy sector, aluminum paste plays a crucial role in the production of solar cells. The reflective properties of aluminum paste help to increase the efficiency of solar cells. When applied to the back surface of a solar cell, the aluminum paste reflects light back into the cell. This maximizes the absorption of light and the generation of electricity, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the solar cell.
- Plastics: Aluminum paste is also used in the plastics industry. When mixed with plastic, it can provide a metallic look to the plastic product, enhancing its visual appeal. Additionally, aluminum paste can enhance the thermal conductivity of plastic materials. This is particularly useful in electronic devices where heat dissipation is crucial for the device’s performance and longevity.
- Inks: In the printing industry, aluminum paste is used in certain types of inks to provide a metallic finish. This metallic ink is used in packaging and label printing, adding a touch of luxury and sophistication to the printed material. The reflective properties of aluminum paste also enhance the visibility of the printed text or design, making it more eye-catching.
- Cosmetics: In the cosmetics industry, aluminum paste is used in products like nail polish and eyeshadow to give them a shiny, metallic look. The tiny, flake-like particles of aluminum in the paste reflect light, providing a shimmering effect when applied to the skin or nails. This enhances the aesthetic appeal of the cosmetic product, making it more attractive to consumers.

Safety Considerations When Using Aluminum Paste
While generally safe for its intended use, aluminum paste requires proper handling due to the presence of aluminum flakes and the carrier medium. Here’s a detailed breakdown of key safety considerations:
Respiratory Protection
- Type of respirator: When working with aluminum paste, it’s crucial to wear a respirator certified by NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) to prevent inhaling dust particles.
- Selection criteria: The specific type of respirator needed depends on the concentration of aluminum flakes in the air. For most applications, a disposable N95 respirator will be sufficient. However, if working in a highly concentrated environment or with a solvent-based paste, a powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) might be necessary.
- Fit testing: Ensure the respirator fits properly to create a tight seal around your nose and mouth. Conduct fit testing as recommended by the manufacturer or your workplace safety program.
Skin Contact
- Protective clothing: Wear gloves, long sleeves, and pants made from impervious materials like nitrile rubber or butyl rubber. This minimizes skin contact with aluminum paste and the carrier medium.
- Skin irritation: Aluminum paste can cause dryness, redness, and irritation. If skin contact occurs, immediately wash the affected area with soap and water for at least 15 minutes. Remove contaminated clothing and wash it thoroughly before reuse.
- Allergic reactions: In rare cases, individuals may experience allergic reactions to aluminum paste. If you develop any unusual symptoms like persistent itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
Eye Protection
- Safety glasses or goggles: Wear safety glasses or chemical goggles that provide a snug fit and complete eye protection from splashes or airborne aluminum flakes. Consider goggles with indirect ventilation to prevent fogging.
- Eye contact: If aluminum paste gets into your eyes, flush them immediately with clean water for at least 15 minutes. Hold your eyelids open during flushing and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Fire Safety
- Flammability: Aluminum paste, particularly solvent-based varieties, can be flammable due to the organic solvents used in the carrier medium.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your working area to prevent the buildup of solvent vapors. Local exhaust ventilation is highly recommended.
- Storage: Store aluminum paste in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat sources, open flames, and sparks. Keep containers tightly sealed when not in use.
- Firefighting: In case of a fire, use dry chemical powder or CO2 extinguishers. Water may not be effective for extinguishing fires involving aluminum paste. Always follow established fire safety protocols in your workplace.
Environmental Considerations
- Disposal: Aluminum paste and its containers should be disposed of responsibly according to local regulations. Never pour aluminum paste down the drain or dispose of it with regular waste. Contact your local waste management authority or a licensed hazardous waste disposal company for proper disposal procedures.
- Water-based alternatives: Whenever possible, choose water-based aluminum pastes to minimize environmental impact. Water-based options are generally less hazardous and easier to dispose of responsibly compared to solvent-based varieties.
By following these safety considerations, you can minimize risks associated with handling aluminum paste and ensure a safe working environment. Remember, always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific aluminum paste you are using for detailed safety information and handling procedures.

Conclusion
Aluminum paste is a valuable industrial material with a wide range of applications. Understanding its composition, types, manufacturing process, and safety considerations allows for its safe and effective utilization in various industries. From enhancing the aesthetics of everyday objects to contributing to specialized industrial processes, aluminum paste plays a vital role in our world. As research and development continue, we can expect even more innovative applications for this versatile material.