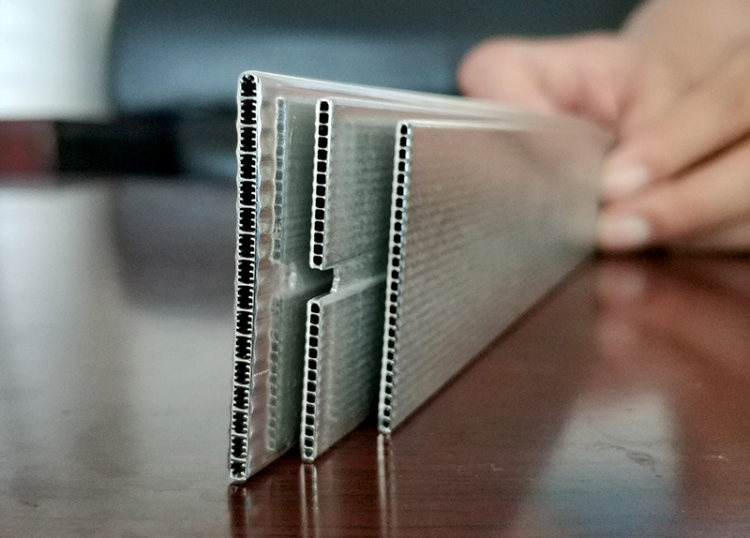
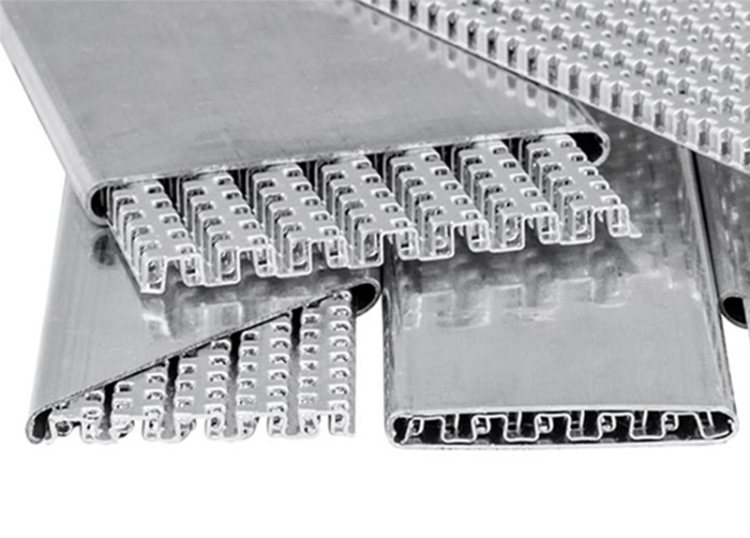
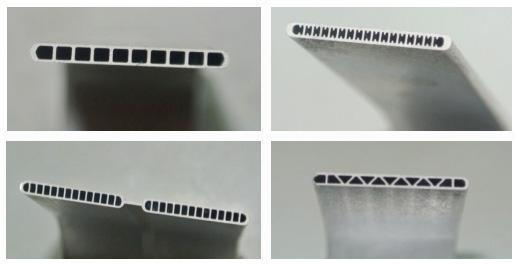
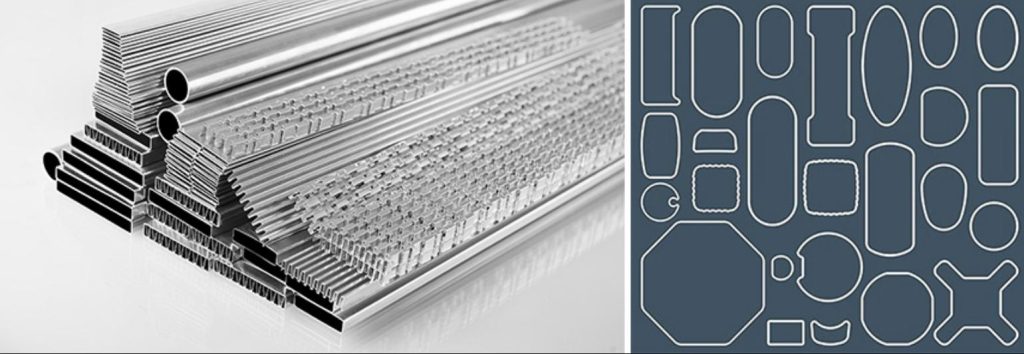
Aluminum condenser header pipes have become a popular choice in refrigeration and air conditioning systems due to their unique properties and performance characteristics. These essential components play a vital role in the heat exchange process, facilitating the transfer of heat from the refrigerant vapor to the surrounding air. In this article, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of using aluminum condenser header pipes, shedding light on why they are favored in certain applications and the considerations that need to be taken into account.

Advantages of Aluminum Condenser Header Pipe
- Excellent Heat Transfer Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of using aluminum condenser header pipes is their exceptional heat transfer efficiency. Aluminum is renowned for its high thermal conductivity, which means it can rapidly and effectively transfer heat between the refrigerant vapor and the ambient air. This results in improved cooling performance, ensuring that the system operates at optimal efficiency.
- Lightweight Construction
Aluminum is a lightweight metal compared to traditional materials such as copper. This characteristic significantly reduces the overall weight of the condenser unit, making it easier to handle during installation and maintenance. Moreover, the reduced weight can lead to cost savings in terms of transportation and handling expenses.
- Corrosion Resistance
Another noteworthy advantage of aluminum condenser header pipes is their natural corrosion resistance. When exposed to the atmosphere, aluminum forms a thin oxide layer on its surface, which acts as a protective barrier against corrosion and rust. This inherent resistance to corrosion ensures that the header pipe maintains its structural integrity over an extended period, enhancing the system’s longevity.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Aluminum is generally more cost-effective than other metals like copper, which is commonly used in condenser coils. The lower cost of aluminum makes it an attractive option, especially for larger cooling systems that require a considerable amount of material. This cost-effectiveness can translate into more affordable air conditioning and refrigeration solutions for consumers and businesses alike.
- Eco-Friendly and Recyclable
As the world shifts toward sustainable practices, the use of aluminum condenser header pipes aligns with environmental conservation efforts. Aluminum is highly recyclable, and its recycling process requires significantly less energy compared to producing new aluminum from raw materials. This recyclability reduces the environmental impact of HVAC systems, making them more eco-friendly.

Disadvantages of Aluminum Condenser Header Pipe
- Reduced Mechanical Strength
While aluminum offers several advantages, it is not as mechanically robust as materials like copper or stainless steel. Aluminum condenser header pipes may be more susceptible to damage during handling, installation, or if subjected to physical stress during the system’s operation. Proper care and precautions are necessary to ensure the longevity of the aluminum pipes.
- Risk of Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion can occur when aluminum comes into direct contact with dissimilar metals, such as copper or steel. This phenomenon can lead to accelerated corrosion of the aluminum condenser header pipe, compromising its functionality and structural integrity. Engineers and manufacturers need to carefully design the system to prevent galvanic corrosion by using suitable insulating materials or protective coatings.
- Vulnerability to Formicary Corrosion
Formicary corrosion, commonly known as “ants’ nest corrosion,” is a specific type of corrosion that can affect aluminum coils when exposed to certain organic acids. This corrosion can create tiny, pinhole-sized cavities within the condenser pipe, reducing its efficiency and potentially causing refrigerant leaks. Appropriate preventive measures, such as selecting corrosion-resistant coatings and materials, are crucial to mitigate this risk.
- Limited Compatibility with Certain Refrigerants
While aluminum is compatible with many refrigerants, certain high-pressure and high-temperature refrigerants may not be suitable for use with aluminum condenser header pipes. Exposure to these refrigerants may cause damage to the aluminum material over time. In such cases, alternative materials like copper or stainless steel may be preferred.
- Sensitivity to Acidic Environments
Aluminum is sensitive to acidic environments and certain chemicals. Exposure to acidic substances can lead to accelerated corrosion of the aluminum condenser header pipe, compromising its structural integrity and efficiency. Proper maintenance and monitoring of the system’s operating conditions are necessary to prevent such issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aluminum condenser header pipes offer several advantages, including excellent heat transfer efficiency, lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. However, they also come with considerations such as reduced mechanical strength, vulnerability to certain types of corrosion, and limitations with certain refrigerants. Proper design, material selection, and maintenance practices are crucial to harnessing the benefits of aluminum condenser header pipes while addressing potential drawbacks. By understanding the strengths and limitations of these components, HVAC professionals can make informed decisions to optimize the performance and reliability of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.