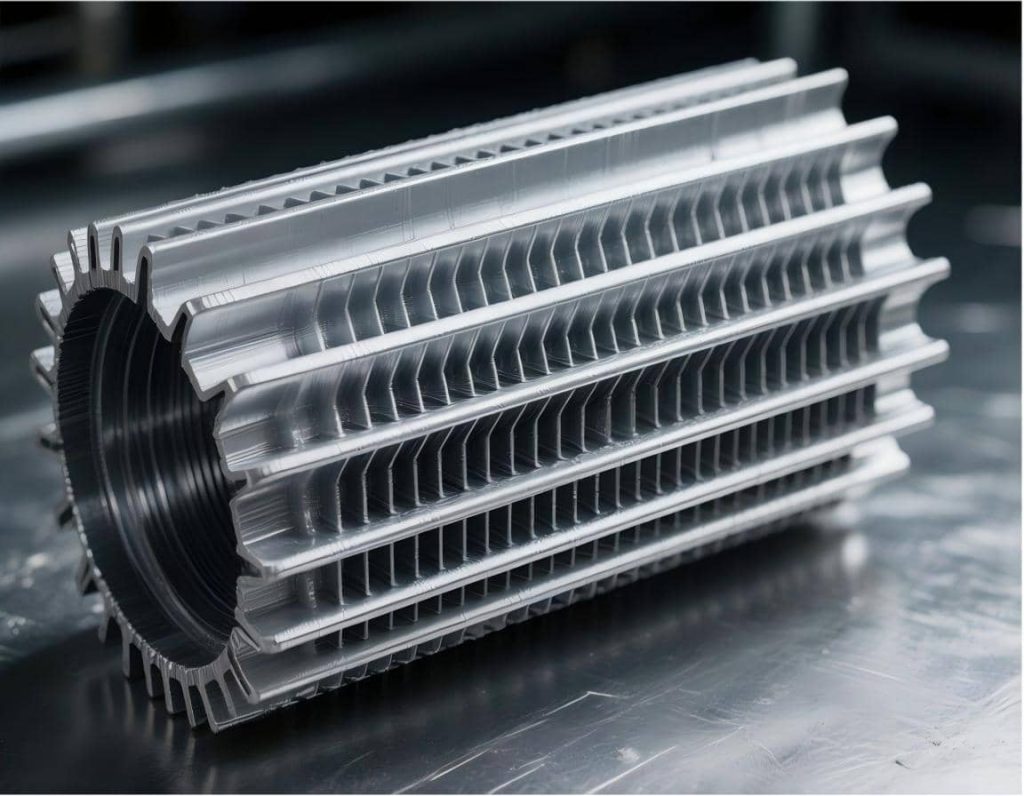
The future of the global aluminum markets is not defined by total capacity but rather by the precision and quality strategy. Previously, the market was characterized by construction profiles and general-purpose pipes. Today, aluminum tubing is becoming increasingly popular due to its high-tolerance and multifunctional applications in electric cars, AI labs, aerospace, and medical industries.
This change is imposed by three pushing elements: the objectives of becoming carbon-neutral globally, the increasing power of AI, and the increase of electrified mobility. Since systems are increasingly becoming smaller, hotter and more integrated, the previous coating of aluminum tube and some similar others can no longer achieve the desired functionality. So, they are essential in the development of the high precision aluminium extrusion tubes and high precision aluminium tubes required for the next generation thermal and structural designs.

From Traditional Extrusion to Precision Manufacturing
1. What Defines High-Tolerance Aluminum Tubing?
In traditional methods of aluminum extrusion, significance is given mostly to accuracy in shape and the speed of mass production. For tube-and-fin heat exchangers, battery cooling systems, or microchannel systems, a variation of 0.1 mm does not cut it.
High-tolerance aluminum tubing is defined by:
- Ultra-tight wall thickness control (±0.02 mm or better)
- High concentricity and straightness
- Uniform surface roughness
- Consistent mechanical properties along the tube length
Achieving this requires more than improved dies. Modern precision extrusion integrates optimized alloy flow simulation, real-time dimensional monitoring, controlled cooling, and post-extrusion stretching. The result is aluminum tubing that behaves as a functional engineering component, not a commodity material.
Minimally invasive surgery equipment, space exploration sensor coverings, and process fluids delivery pumping systems are among the most common applications where reliability and dimensional stability are required.
2. Ultra-Thin Wall and Micro-Channel Extrusion (MPE)
In the field of precision extrusion, one of the newest developments is the increase in the number of orifices – multi-port extrusion (MPE). MPE ensures that the aluminum tubes have a number of interior micro-channels that significantly enhance the heat transfer area of the tubes without necessarily increasing their bulk or weight.
In advanced thermal systems, wall thicknesses can be reduced to 0.2–0.3 mm, enabling rapid thermal response. However, not all aluminum alloys are suitable for such structures. Alloy fluidity, grain refinement, and extrusion stability determine whether micro-channel designs are achievable at scale.
This limitation makes alloy selection just as important as extrusion capability.

Alloy Innovation: Why 7003 Aluminum Is Gaining Momentum
1. Overview of 7003 Aluminum Alloy
7003 aluminum alloy is a member of the Al-Zn-Mg-Zr family, and is best known for use where it is important to have applications with good stretch forming properties.
Unlike traditional 6000-series alloys, 7003 offers:
- Significantly higher yield and tensile strength
- Improved fatigue resistance
- Better structural performance under dynamic loads
Since the characteristics listed for the 7003 aluminum tubing make it an attractive alternative for the structural-integrated thermal systems, more so in electric vehicles.
2. Heat Treatment and Performance Balance (T5 vs. T6)
7003 aluminum tubes are commonly supplied in T5 or T6 temper, each offering a different balance:
- T5: Higher extrusion efficiency, good strength, lower cost
- T6: Maximum mechanical strength after solution treatment and aging
This feature enables the manufacturer to modify the tubing performance for various parameters such as pressure, safety, lifecycle—very important in modern systems of heat management.
Thermal Management Comparison: 6063 vs. 7003 Aluminum Tubes
Choosing the right alloy often comes down to a balance between thermal efficiency and structural safety. The table below summarizes the key differences.
| Performance Dimension | 6063 Aluminum (T6) | 7003 Aluminum (T5/T6) | Application Impact |
| Alloy Series | 6000 (Al-Mg-Si) | 7000 (Al-Zn-Mg-Zr) | Base mechanical behavior |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 200–218 | 130–150 | 6063 dissipates heat faster |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 170–214 | 300–360 | 7003 resists deformation |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 185–240 | 350–400 | 7003 suits high-stress systems |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good | 6063 more stable in long-term liquid loops |
| Extrusion Complexity | Excellent | Good | 6063 ideal for micro-channels |
| Typical Applications | AI cold plates, heat exchangers | EV battery cooling, pressure manifolds | Selection based on use case |
- 6063 aluminum dominates applications where maximum heat transfer and micro-channel precision are required.
- 7003 aluminum excels in environments where pressure resistance, crash safety, and structural integration are critical.
This explains why the two alloys rarely compete directly—instead, they serve complementary roles in advanced thermal systems.

The Key Applications of 7003 Aluminum Tubes in New Energy Vehicles
1. Battery Cooling Plates and Structural Integration
More recently developed NEVs are increasingly making the transition to CTP and CTC architectures. In so doing, the battery cooling plates are no longer standalone thermal components, but they are part of the structure of the vehicle, serving the purpose of crashworthiness.
This dual requirement makes 7003 aluminum tube for EV battery cooling a preferred solution:
- High yield strength improves impact resistance
- Superior pressure tolerance supports fast-charging liquid cooling
- Lightweight construction enhances vehicle efficiency without sacrificing safety
As battery energy density increases, these advantages become increasingly decisive.
Heat Pump Systems and CO₂ Refrigerants
Additionally, one of the transformations is the incorporation of CO₂ refrigerants into the EV’s heat pumps. Because CO₂ is employed at much higher pressures than regular refrigerants, means that tubing materials must meet extreme conditions.
Precision-extruded 7003 aluminum tubes, which are typically designed with deeper walls or interior reinforcements, offer an excellent balance of safety, mass, and ease of fabrication and are, therefore, very promising for the design of new generation thermal circuits.

Aluminum Tubes for Powering Liquid-Cooled Data Centers
1. Why Liquid Cooling Is Becoming Standard
By 2026, AI training clusters and high-density GPU servers are pushing power densities beyond what air cooling can handle. As a result, cold plate liquid cooling and immersion cooling are becoming standard in modern data centers.
2. Aluminum Tubes in Liquid Cooling Data Centers
In liquid-cooled facilities, aluminum tubes perform several critical roles:
- Coolant distribution pipelines in CDU systems
- Manifolds connecting server cold plates
- Return and balancing lines within cooling loops
Compared to copper, aluminum tube for liquid cooling data centers offers:
- Lower material cost
- Significant weight reduction
- Easier installation in modular data centers
High cleanliness standards and controlled corrosion behavior are essential, making precision extrusion and surface treatment key success factors.
3. Power Transmission and Tubular Busbars
Beyond cooling, aluminum tubes are increasingly used in tubular busbar systems for high-current power distribution. Their geometry helps optimize skin effect behavior at high frequencies, while maintaining structural rigidity and heat dissipation—an important advantage in AI data centers with fluctuating loads.

Wrap Up
The precision aluminum extrusion tubes have been evolving far from static to strategic engineering system components addressing thermal management, strength, safety, and ecological related aspects.
The performance and reliability of the system can now be attributed to the appropriate combination of alloy selection and precision manufacturing during the design and development of EV battery systems, AI liquid-cooling data centers, advanced industrial equipment, and so on.