The manufacturing industry has benefited a lot from aluminum, one of the most widely used metals. Aluminium has frequently been utilized in consumer goods for the food and beverage industry, as well as household items. Such as foil, pots, pans, baking trays, and similar items. Aluminum also has been widely used in construction and other industries, such as building, to create electrical wiring, paneling, and roofing materials that are resistant to corrosion. Those are realized by drawn and extruded aluminum processes.
Despite their similarities, drawn aluminum and extruded aluminum differ significantly in some important ways. Knowing about these variations can assist you in selecting the best one for your upcoming job.

Drawn Aluminum vs Extruded Aluminum: Definition
- Drawn Aluminum
Any type of aluminum product created through deep drawing can be referred to as drawn aluminum. In this sheet metal procedure, a blank is produced by punching. As the sheet metal is secured over to a durable tool, hydrostatic pressure is used to form the shape.
The ability to construct shapes with components whose depth extends over the part’s circumference is provided by deep sketching. It could produce products with tight tolerances and accurate dimensions that are either symmetrical or asymmetrical.
- Extruded Aluminum
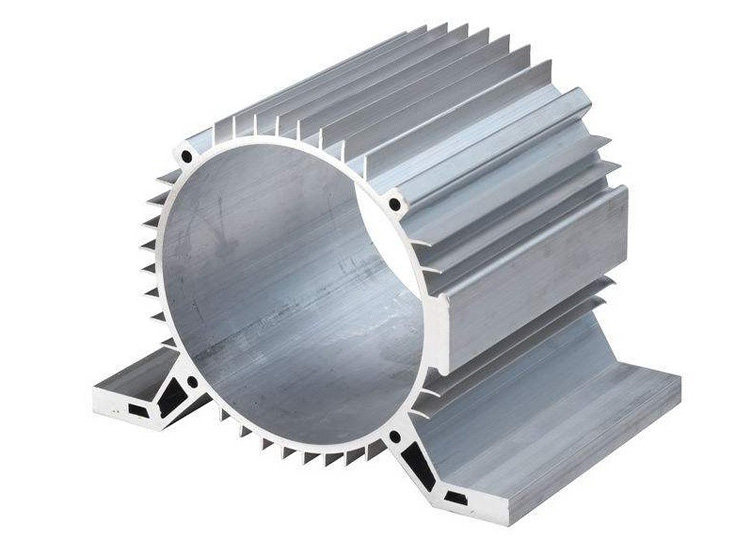
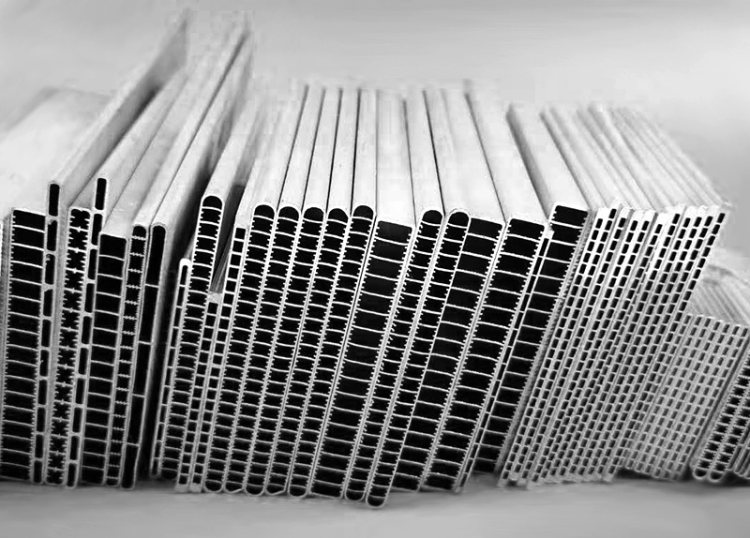
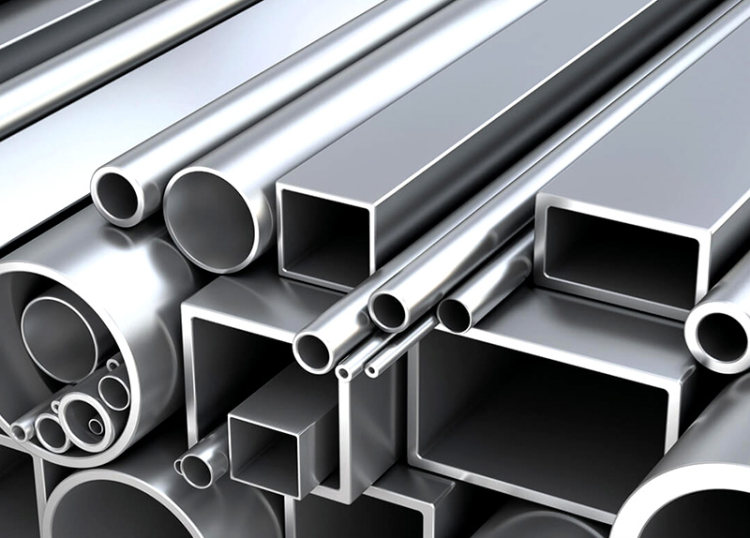
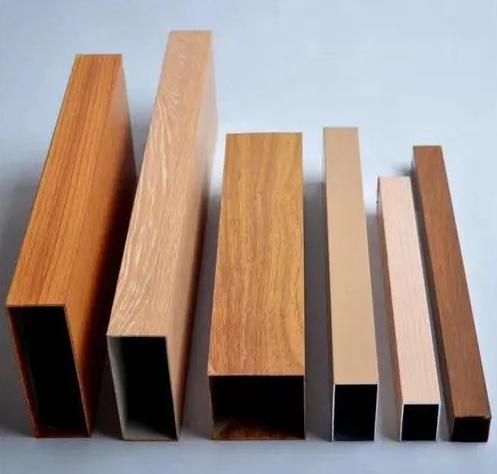
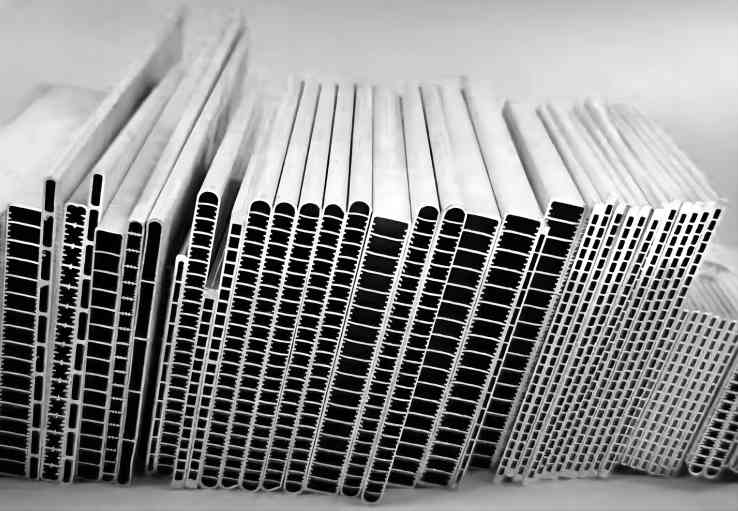
Extruded aluminum is the aluminum materials with different cross-sectional shapes obtained by hot-melting and extruding aluminum rods. The production process of aluminum profiles mainly includes three processes: casting, extrusion and coloring. Coloring mainly includes: oxidation, electrophoretic coating, fluorocarbon spraying, powder coating, wood grain transfer and other processes.
Drawn Aluminum vs Extruded Aluminum: Application
- Drawn Aluminum
Drawn aluminium is ideal for products requiring tight tolerances and thin walls, ensuring structural integrity and predictable performance under pressure. For instance, Intricate or circular objects such as cans, tubes, pots and pans.
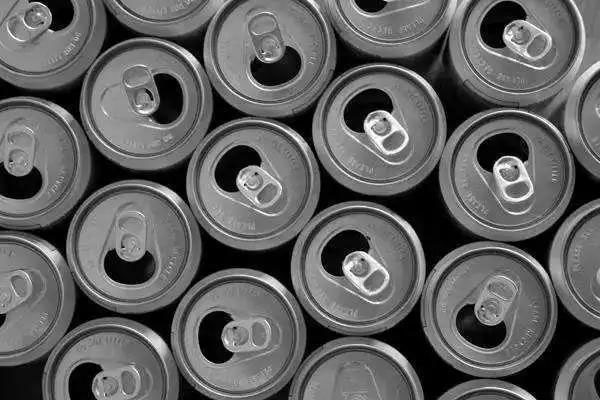

- Extruded Aluminum
Aluminum is forced through a shaped opening in a die or mold, creating the required configuration of the finished product. Consider modeling clay used by youngsters to visualize the procedure, consider modeling clay used by children. It comes with a shape tool kit with various molds and profiles. Choose a particular profile; insert the clay via the specially formed hole, and the clay emerges in the expected shape, resulting in extruded aluminum.
For extruded aluminium, there’s a considerable capacity to shape various applications, such as brackets, tubing, doors, window frames, railing and much more.
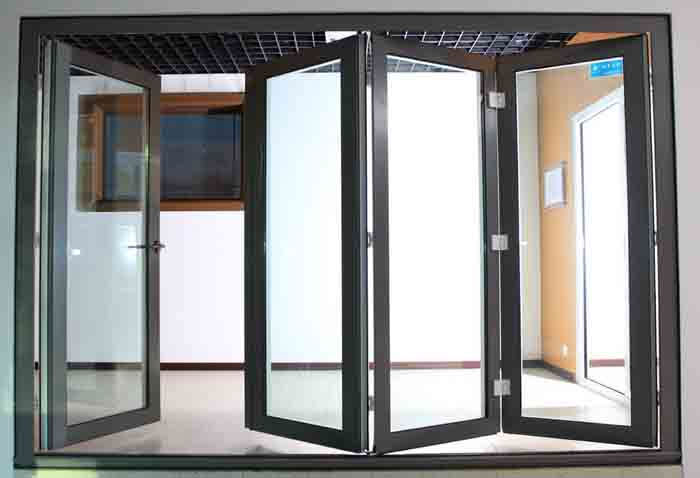

Drawn Aluminum vs Extruded Aluminum: Process
- Drawn Aluminum
The drawn aluminum tubing technique involves pulling or drawing the aluminum into the die chamber, where it goes through a process known as plastic deformation. When metal is stretched to create the desired shape, plastic deformation occurs. It’s critical to pay special attention to the metal’s flexibility and elasticity when stretching aluminum. It will become weak and brittle if you stretch it too much. The most typical products made from drawn aluminium are pots, cans, tubes, and other rounded items.

- Extruded Aluminum
Extruded aluminum differs from drawn aluminum in that the formed shape is made by first heating the metal to a very high temperature until it is soft and malleable but not liquid. The aluminum is heated before being pushed or shoved into a die. The die will mold and shape the extruded metal tubing that emerges from the opposite end into the final shape that is wanted. Imagine a toothpaste tube to help you understand the extrusion process. In this instance, the circular aperture through which the toothpaste is pumped shapes the toothpaste. The metal will start to cool and harden once it has been extruded.
The finished extruded tubing product hardens to a strong, resilient state that will keep the desired shape.

Which is the Better Choice with Cost?
Drawn aluminum has various drawbacks even though the technique is quite beneficial for making specialty parts with conical or spherical geometries. To avoid deforming the material, the drawing needs to be done, among other things, carefully. Despite being pliable, aluminium can shatter and suffer other damage if it is drawn far beyond the permitted limits.
These factors contribute to the fact that drawn aluminium products are often more expensive than their extruded counterparts. Manufacturers would still need to take into account additional parameters, such as alloying components, aluminum quality, and the strengthening procedure that will be employed, before stretching the material.
In this case, extrusion might be the more economical choice due to the process’ ability to drastically reduce the price of the finished good. The task requires fewer materials, which lowers costs and improves process efficiency. Additionally, several grades of aluminum, including 1060, 3003, 6061, 6063, and many more, can be employed for the task.
Aluminum extrusion is a superior option to obtain a variety of aluminum parts at a reasonable price if you have financial constraints for your project.

Conclusion
Drawn and extruded aluminum are both capable of generating high-quality finished parts for OEM, custom, or aftermarket applications. Products made of drawn aluminum can come in a wide range and satisfy both domestic and international quality standards. The same can be said about extruded aluminum, which has several uses in daily life.
You can select between the two approaches in terms of quality. However, you should be aware that drawn aluminum has its limitations and is only appropriate for parts with simple designs. In contrast, there are countless chances to create unique designs with extruded aluminum.