In the world of engineering and technology, managing heat is a critical endeavor. Whether it’s protecting sensitive electronic components, ensuring the efficiency of automotive systems, or enabling aerospace exploration, effective heat management is a necessity. Aluminum heat shields, designed to dissipate and protect against excessive heat, rely heavily on the type and thickness of the aluminum profile used in their construction. These factors significantly influence the heat shield’s overall performance and effectiveness.
What are the Advantages of Aluminum?
Aluminum, known for its lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity, is a go-to material for heat shield construction. Its ability to rapidly transfer and disperse heat makes it an ideal choice for applications where temperature control is paramount. However, the effectiveness of an aluminum heat shield isn’t solely determined by the material; the design of the aluminum profile used plays a vital role.
What Types of Aluminum Profiles Used in Aluminum Heat Shield?
Aluminum profiles are essentially customized shapes that enhance the structural and thermal capabilities of heat shields. Different profile types offer varying benefits, aligning with specific applications and heat management requirements:
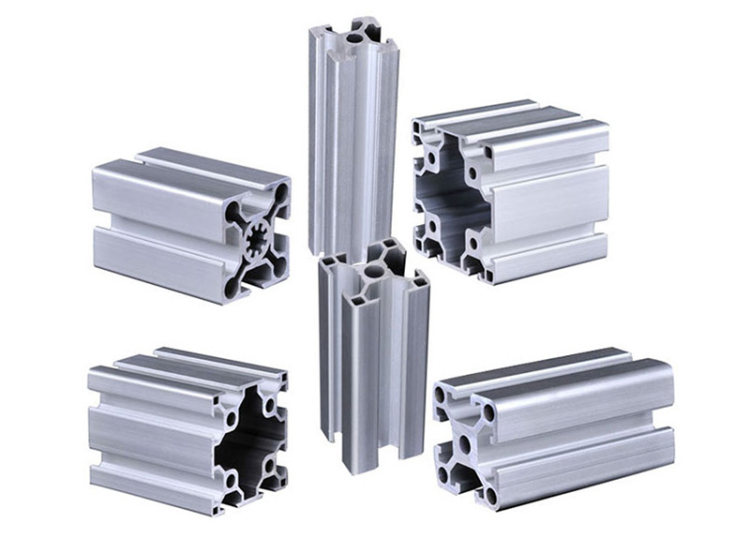
- Extruded Profiles: These profiles are crafted by pushing heated aluminum through a die to create specific cross-sectional shapes. Extruded profiles offer versatility in design, making them adaptable for various heat shield needs. Their intricate designs allow for optimized heat dissipation, a crucial factor in scenarios where rapid heat transfer is essential.
- Tubular Profiles: Tubular aluminum profiles, resembling pipes or tubes, are particularly valuable in applications requiring fluid or air cooling. Their cylindrical shape facilitates the passage of coolant or air, thereby enhancing heat dissipation through convection.
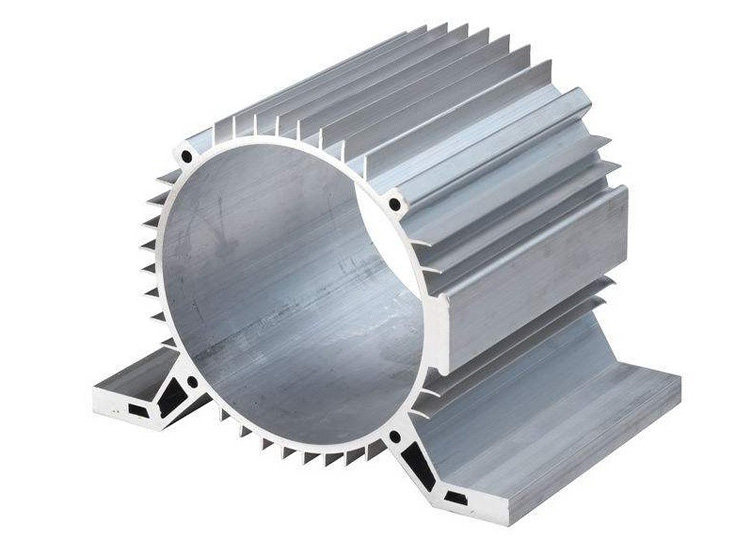
- Finned and Louvered Profiles: Finned and louvered profiles introduce extended surface elements, effectively increasing the profile’s surface area. This design promotes enhanced heat transfer through both conduction and convection, rendering them ideal for situations demanding high heat dissipation rates.
- Hollow Section Profiles: Characterized by a closed box-like shape, hollow section profiles strike a balance between structural integrity and heat management. These profiles often serve as both thermal barriers and load-bearing components, making them suitable for dual-purpose requirements.
- Custom Profiles: Tailored to meet specific heat management needs, custom profiles integrate unique features like grooves, ridges, or channels. This level of customization optimizes heat dissipation for specialized applications.
How Does the Thickness of an Aluminum Heat Shield Affect its Performance?
Beyond profile type, the thickness of the aluminum profile is another pivotal aspect impacting heat shield performance. Thickness affects multiple attributes of the heat shield:
- Thermal Insulation: Thicker profiles offer superior thermal insulation, effectively slowing down the rate of heat conduction. This property is particularly valuable when protecting heat-sensitive components from extreme temperatures.
- Heat Capacity: A thicker profile boasts higher heat capacity, allowing it to absorb more heat energy before reaching critical temperatures. This characteristic proves advantageous in scenarios involving intermittent or fluctuating heat sources.
- Heat Transfer Resistance: Increased thickness results in higher thermal resistance, which reduces the rate of heat flow through the heat shield. This feature proves beneficial when minimizing heat transfer between two environments is crucial.
- Weight Considerations: While thicker profiles provide enhanced insulation, they also contribute to increased weight. Designers must strike a balance between desired thermal performance and overall system weight.
The relationship between aluminum profile type and thickness is not isolated; rather, they often work synergistically to optimize heat shield performance. For instance, a finned or louvered profile with increased thickness can effectively enhance both heat dissipation and thermal insulation, offering a multifaceted solution to heat management challenges.
Application Across Industries
The influence of aluminum profile type and thickness transcends industries. In the automotive sector, finely tuned heat shields constructed with specific profiles and thicknesses ensure efficient cooling of exhaust components, preventing overheating and improving vehicle performance. In the realm of electronics, customized hollow section profiles offer structural support while safeguarding delicate circuitry from thermal stresses.
In Conclusion
The dynamic interplay between the type and thickness of the aluminum profile is pivotal in determining the effectiveness of an aluminum heat shield. The right combination of profile type and thickness can significantly enhance heat dissipation, structural integrity, and thermal insulation. As we journey further into a world demanding advanced thermal management solutions, understanding the intricate relationship between these parameters paves the way for innovative applications across diverse industries. The collaborative power of aluminum profile type and thickness ensures the integrity and longevity of heat shields in the face of relentless thermal challenges, underscoring the role of these shields as unsung heroes of modern engineering.